July 29, 2024 - Radiation: What You Should Know
UV rays, old televisions, smoke detectors, granite countertops, and x-rays. What do these have in common? They’re all radioactive - to a certain degree. Truthfully, radiation is everywhere. Thanks to science and strict monitoring there are ways to figure out when concern is warranted. Becoming familiar with the classifications of radiation - ionizing and non-ionizing - is the first step in remaining safe.
Ionizing radiation, otherwise known as nuclear radiation, has high enough energy to ionize molecules and cause biological damage. Common sources of ionizing radiation include the following: UV rays, cosmic particles, radon gas, medical imaging, smoke detectors, potassium-enriched fertilizers, food sterilization methods, and forms of technology that utilize radionuclides (within professional environments). Other natural sources of radiation that emit doses much too low to cause harm are called background radiation.
To better understand risk it’s helpful to know that the average person not working with radioactive material typically absorbs a background dose of 0.1 to 0.2 rem/year (0.001 to 0.002 Sv/yr or 100,000 to 200,000 μR/yr). Taking this into account comparisons can be made via the tables below:
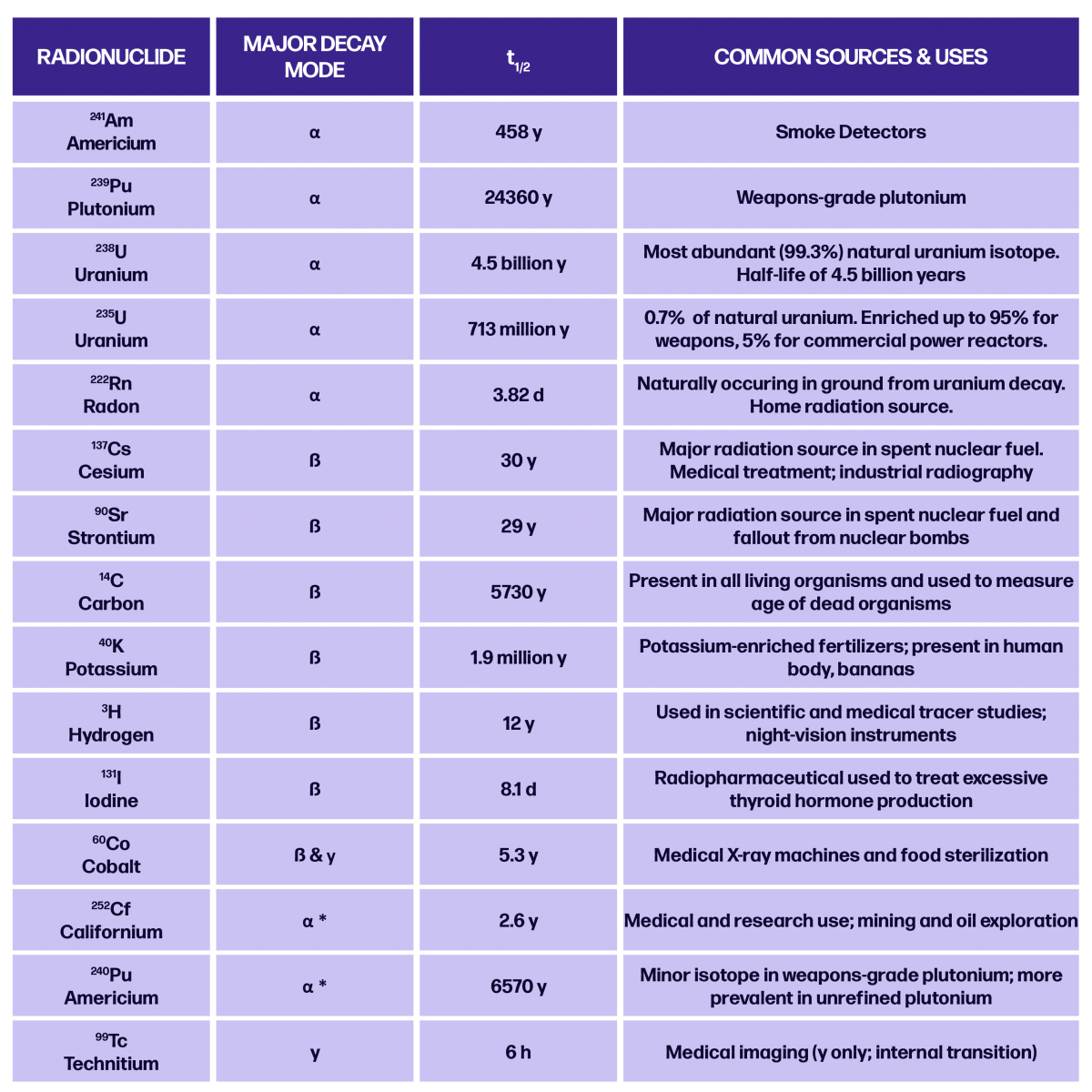
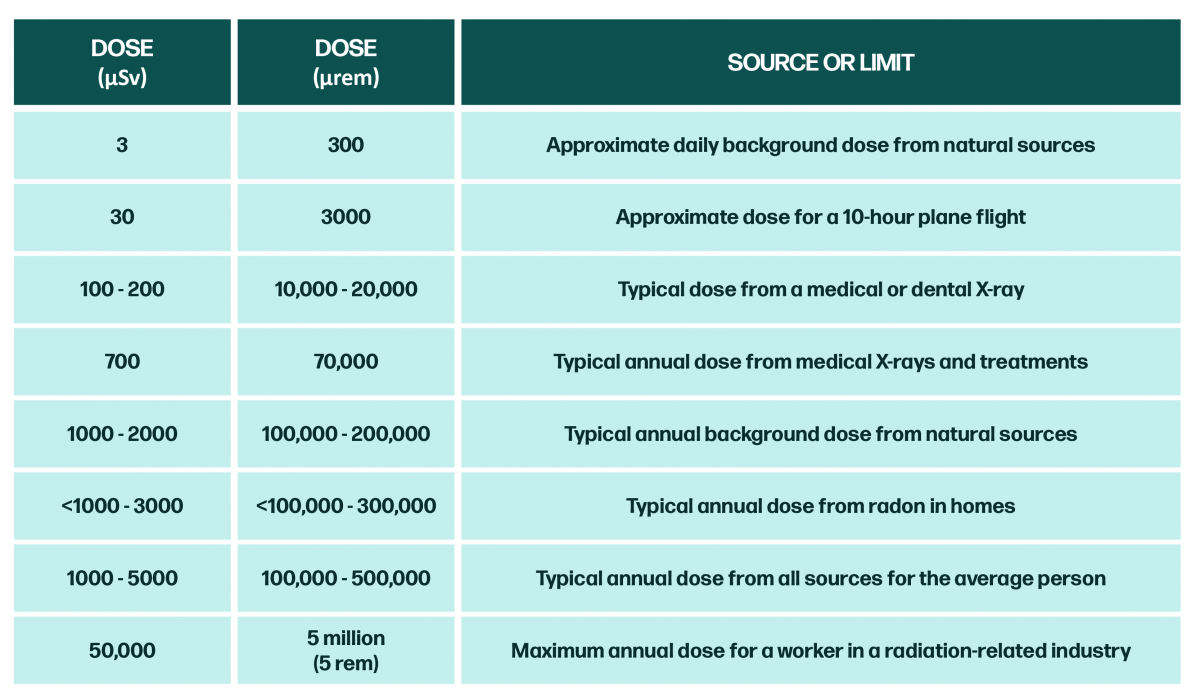
Non-ionizing radiation is the second classification of radiation and is generally considered harmless because its photon energy or intensity is so low. Radio & TV waves, cell phones, and microwaves are in this category of radiation (Huie, D. et al.). However, non-ionizing radiation hasn’t been written off entirely. Several occurrences have shown possible associations between power lines, cell phone use, and use of high-energy equipment with certain types of cancer (BCPP). Current ongoing studies of exposure to electromagnetic radiation produced by mobile phones and other technology suggest a possible correlation between long-term EMR exposure and weakened immune response (M. E. López-Martín et al.) While the definite results remain inconclusive for several reasons, the public can keep up to date with findings through the EPA’s RadTown radiation education website
linked here.
Our bodies have mechanisms to reverse the effects of radiation but damage is cumulative as our mechanisms weaken over time. This is why it’s important to remain aware of radiation sources and to learn what can be done to minimize risk. For example, radon gas poisoning is a leading cause of lung cancer yet can easily be measured with a RAD device and prevented by ensuring a building is properly sealed and ventilated (WHO). Sun damage is another form of radiation that can easily be prevented with the use of sunscreen and sun-blocking clothing. Learning about risk and making even a small lifestyle change can make a huge difference.
Even under heavy precautions accidents happen. Hazmat teams and first responders carry radiation detection devices to put in use when there is a spill or other type of disaster. Security personnel typically utilize RIIDs to ensure that arenas or other large public events spaces are clear of dangers. To our benefit, remote learning opportunities are also plentiful to learn more about what to do in the event of an emergency and how to best prepare.
Citations
US EPA (2024, June 25). US EPA. RadTown. In United States Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/radtown
BCPP (2024, May 30). Non-Ionizing Radiation. In Breast Cancer Prevention Partners (BCPP). https://www.bcpp.org/resource/non-ionizing-radiation/
Huie, D., Lerner, E. C., Edwards, R. M., Srinivasan, E. S., Vaios, E. J., & Fecci, P. E. (2022). Advanced Imaging techniques and planning for laser interstitial thermal therapy. In Elseview eBooks (pp. 285-301). http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-822835-7.00054-8
M. E. López-Martín, R. A. Sueiro-Benavides, J. m. Leiro-Vidal, J. A. Rodríguez-González and F. J. Ares-Pena (2023). Can electromagnetic fields modulate inflammation and cell death by acting on the immune system? In IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10229142/citations#citations
World Health Organization: WHO. (2023, January 25). Radon. In WHO. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/radon-and-health#:~:tex...
